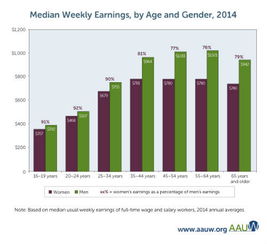
中国与美国家庭的差异
Title: Understanding Legal Differences Between China and the United States
Legal systems play a fundamental role in shaping societies, and understanding the differences between them is crucial, especially in the context of global interactions. This article explores the key disparities between the legal systems of China and the United States, shedding light on their distinct features and implications.
In China, the legal system is primarily based on civil law, heavily influenced by Confucianism and socialist principles. It emphasizes the role of statutes and administrative regulations in governing society. On the other hand, the United States follows a common law tradition, which relies on judicial precedent and case law to interpret statutes and shape legal principles.
Legislation in China is promulgated by the National People's Congress (NPC) and its Standing Committee. Laws cover a wide range of areas, including civil, criminal, administrative, and commercial law. In contrast, the United States Congress passes federal laws, while state legislatures are responsible for enacting laws at the state level. This division of legislative power between federal and state governments is a hallmark of the U.S. legal system.
Judicial independence is a cornerstone of the legal systems in both countries, but the mechanisms differ. In China, the judiciary is subordinate to the Communist Party, leading to concerns about the impartiality of courts, especially in politically sensitive cases. Conversely, the United States prides itself on the separation of powers, with an independent judiciary that serves as a check on the executive and legislative branches.
Protecting individual rights is a central tenet of legal systems worldwide. In China, while the Constitution guarantees certain rights, enforcement can be inconsistent, and political considerations may override legal protections. In contrast, the U.S. Constitution and its Bill of Rights provide strong safeguards for individual liberties, including freedom of speech, religion, and due process. The U.S. legal system offers robust mechanisms, such as judicial review, to remedy violations of rights.
Legal procedures in China often involve bureaucratic hurdles and administrative processes, reflecting the country's emphasis on social stability and centralized control. Court proceedings may lack transparency, and legal representation is not always accessible to all. In contrast, the U.S. legal system places a premium on due process and transparency, with adversarial proceedings and extensive protections for defendants' rights.
Protecting intellectual property is vital for fostering innovation and economic development. China has made strides in strengthening its legal framework for IPR protection, but challenges persist, including enforcement issues and intellectual property theft. In contrast, the United States has wellestablished laws and enforcement mechanisms to safeguard intellectual property, which has contributed to its innovationdriven economy.
Understanding the legal disparities between China and the United States is essential for businesses, policymakers, and individuals engaged in crossborder activities. While both countries have distinct legal traditions and principles, fostering mutual understanding and cooperation can help navigate the complexities of global legal frameworks.